Turning a Patient to the Lateral Position and Prone Position
Subject: Fundamentals of Nursing

Overview
Turning a Patient to the Lateral Position and Prone Position
Purpose
- To ensure comfort of the patient.
- To perform procedures such as changing the linen and giving the bed pan.
- To offer relief on pressure points in the supine position.
Procedure
- Explain to the patient what will be done and how it would help.
- Provide privacy, adjust bed level, and wash hands.
- Position yourself and the patient appropriately before the procedure.
- Move the patient to the side of the bed opposite side of the patient will face when turned using pull sheet by shifting gently with help of one or two nurses.
- While standing on the side of the bed nearest the patient, place the patient's near arm across the chest. Abduct the far arm-flexing at the elbow.
- Flex the knees of the leg near you, place the patient's nearest ankle across the far ankle and foot.
- Raise the side rails next to the patient. Go to the other side of the bed.
- Position yourself on the side of the bed towards which patient will turn directly in line with the patient's waist line.
- Include your trunk forward from the hips. Flex your hips, knees and ankles. Assure a broad distance with weight placed on the forward foot.
- Pull/Roll the patient to a lateral position.
- Place one hand on the patient's far hip and one hand on the patient's far shoulder.
- Tighten your gluteal muscles, rock back shifting your weight and abdominal muscles from forward to backward foot. Roll patient to side of the bed to face you. Invol
- To roll on to the prone position, the arm farther to you should be kept alongside the body, when turning roll completely.
Note: Never pull the patient across the bed when the patient is in a prone position as it may injure a woman's breast or a man's genitals.
Log Rolling a Patient
Log rolling is a technique used to turn a patient whose body must at all times be kept in straight alignment e.g. in spinal injury.
Procedure
- Explain the procedure to the client what you are going to do and why it is necessary for him/her.
- Determine the number of nurses needed for the move.
- Wash hands, provide privacy.
- Raise the bed to a comfortable working height.
- Raise the side rail on the far side of the bed.
- Position two nurses on same side of the bed to which the patient will be turned. Position third nurse on the other side of bed.
- Cross the patient's arms on the chest.
- Lean your trunk, and flex your hips, knees and ankles.
- Slide the arms under the client. Tighten your gluteal, abdominal, leg and arm muscles.
- Pull the client to the side of the bed.
- Each nurse should take a smaller region of the body. Each nurse assumes responsibility for one of the three areas: head and shoulder, thigh, hips and ankles. If two nurses are turning the patient, one nurse should lift the neck region and upper body; another nurse should lift the hips and thighs.
- One count one, two, and three go then at the same time all persons pull the client to the side of the bed.
- Elevate the side rail on the side of the bed.
- Move to other side of the bed and place supportive devices for the client when turned.
- Place a pillow where it will support the client's head after the turn.
- Place pillows between the client's legs to support the upper leg when the client is turned.
- Roll and position of the client in proper alignment.
- The nurse on the opposite side of the bed places pillows along the length of the patient.
- Gently lean the patient as a unit back towards the pillows to support along the length of the patient.
- Ensure continued straight alignment of the spinal column preventing injury.
- Put up the side rails on either side.
- Make the patient in a comfortable position.
- Perform hand washing.
- Record the procedure in nurse's notes.
Procedure
- hand washing
- Describe the process.
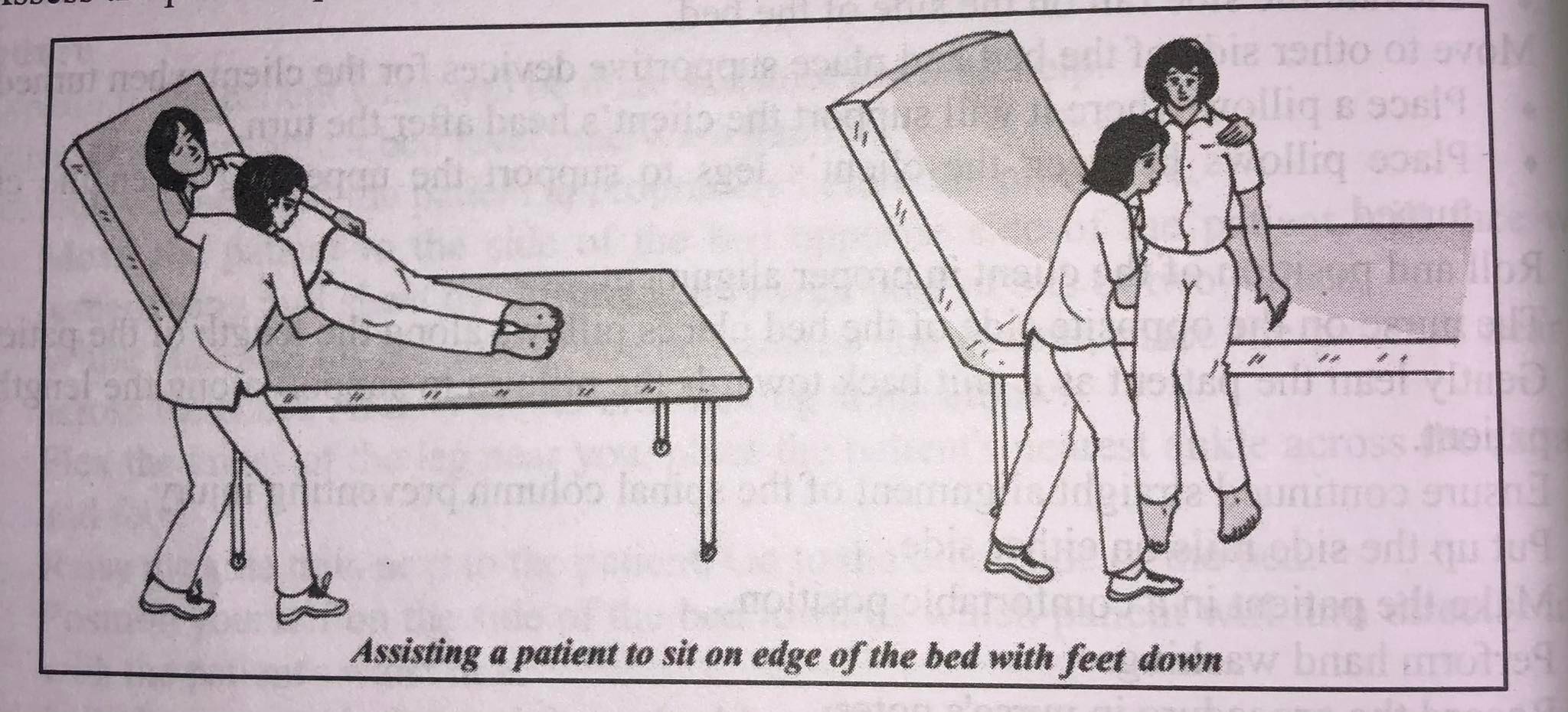
- Place the patient on the side of the bed they will be seated on, lying on their side with their back to you.
- Raising the head of the bed as high as the patient can bear is advised.
- When facing the patient and the far corner of the bed's foot, pivot diagonally while standing opposite the client's hip. bed sling or od
- A foot should be placed in front of another foot, near to the bed's head.
- Put the arm closest to the head of the bed under the patient's shoulder that is supporting their head and neck, and place the other hand over their thighs.
- Lower leg and foot of the patient should be moved over the bed's side.
- Allow the patient's upper leg to swing downward as you pivot towards your nearby leg.
- The position and comfort of the patient should be regularly or as needed assessed.
- Till the patient regains balance, stay in front of them.
- The foot board or the floor should be used to support the feet.
- Clean and iron the client's bedding and clothes.
- The position and comfort of the patient should be regularly or as needed assessed.
Transferring a Patient from Bed to a Chair
Procedure
- Explain the procedure to the patient and instruct him on how he has to co-operate.
- Assist the patient to the sitting position on the side of the bed. Position a chair at 450 angles to the bed or parallel with the bed.
- Assess the patient's orthostatic hypotension before moving the client from the bed.
- Assist the patient in putting on sleeves.
- Flex your knees and hip on the line with the patient's knees.
- Reach under the axilla of the patient and place hands on scapula.
- Help the patient up to standing position on count of three.
- Pivot on foot that is farthest from the chair.
- Ask the patient to sit only after he feels the seat of the chair on the back of his knees.
- Instruct the patient to use arm rest of the chair for support if present.
- Flex your hips and knees and lower the patient to the chair.
- Align the patient properly to the sitting position.
- If the patient is to be shifted to a wheelchair, ensure that its wheels are locked and the foot plate is raised.
Transferring a Patient Between a Bed and a Stretcher
Procedure
- Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Wash your hands and dry them.
- Adjust the patient's bed to be in the flat position.
- Raise the bed/stretcher from where the patient is to be transferred to a slightly higher level. Ensure that the wheels of the bed and stretcher are locked.
- Untuck the draw sheet out from both sides of the bed pulling along a flat surface.
- Move the patient to the edge of the bed and place the stretcher parallel to the bed next to the patient.
- Position yourself for transfer. The first nurse should kneel on the bed on the side from the stretcher. The other two nurses should reach over the stretcher holding the draw sheet, one nurse at the head and chest areas of the patient, the other nurse supporting at the waist Thand thigh area.
- Transfer the patient securely to the stretcher.
- Make the patient comfortable, unlock the stretcher's wheels and move the stretcher away from the bed.
- Raise the stretcher's side rails.
- Having four nurses for the transfer reduces the risk of injury to the patient.
Things to remember
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google