Cardiac Bed Making
Subject: Fundamentals of Nursing

Overview
Cardiac Bed Making
A hospital bed prepared for a heart disease case is known as cardiac bed. It is used for the patients with heart diseases or dyspnoea to provide easy breathing for the patient with minimum strain. It is used to help the patient to assume a sitting position, which can afford him the greatest amount of comfort with least strain.
Purposes
- To relieve dyspnoea caused by cardiac diseases.
- To provide comfort to the patient.
- To reduce work load of heart in cardiac diseases.
- To prevent complications.
Articles
- Ordinary bed equipment,
- Additional articles,
- Cardiac table,
- Extra pillows,
- Back rest,
- Air cushion,
- Foot board,
- O2 suctions equipment if needed.
Procedure
| S.N. | Nursing Action | Rationale |
| 1 | Ascertain the need for bed making. | Provides information. |
| 2 | Explain the patient what will be done and how it would help him to be comfortable. | Facilitates patient's cooperation. |
| 3 | Perform hand washing. | Prevents the spread of infection. |
| 4 | Collect articles, fold and arrange the linen on the stool in the order of use. | Facilitate to perform procedure. |
| 5 | Prepare the foundation of the bed as in open bed. | |
| 6 | Place backrest at patient's back and arranges pillows. | Supports the patient's back and provides comfortable position to the patient. |
| 7 | Place the cardiac table in front of the patient, over the blanket and a pillow over it to allow the patient's hands to rest on it. | Helps patient to lean forward. |
| 8 | Assist patient to assume comfortable position in bed. Cover him properly. | Provides warmth to the patient. |
| 9 |
Adjust knee pillow, air cushion and make the patient comfortable.
Arrange pillows on either side of the patient below both arms. Ensure that patient is sitting comfortably in the new position. |
Prevents slipping of the patient and supports the arm. |
| 10 |
Clean and replace the articles. Wash hands. |
Reduces the risk of transmission of microorganisms. |
| 11 | Record the observation made on the patient in the nurse's notes. |
Promotes communication among staff. |
Orthopedic Bed Making
An orthopedic bed is a hard, firm bed for the patient with fracture. Such bed is used for a patient with fracture of the trunk or extremities to provide firm support by the use of firm mattress. It is used for orthopedic patients; fracture board is used under the mattress to provide a firm support for the patient.
Purposes
- To make the patient comfortable.
- To maintain correct position.
- To aid immobilizing the fracture.
- To prevent unnecessary pain.
- To give firm, even support to the fractures limbs and back.
Articles
- All articles required for simple bed,
- Fracture board,
- Sand bags,
- Bed cradle,
- Extra pillows.
Procedure
- Prepare the foundation of the bed as in simple bed.
- Place the fracture board on the cot (bed) in such a way that it is in between boards for aeration.
- Make the patient comfortable and leave the unit tidy.
Amputation Bed
It is a bed in which the upper clothes are divided. Amputation or stump bed or divided bed, which is used by the nurse for the patient after amputation of the lower limb, is necessary to keep the stump visible and elevated. It is used for the patient whose leg is amputated.
Purposes
- To keep the stump in a good position.
- To observe the stump for hemorrhage constantly and apply tourniquet instantly if necessary.
- To ensure more safety and comfort by preventing soiling and staining.
- To prevent jerking movements for the amputated leg.
- To allow the nurse to do repeated procedures such as bladder irrigation without exposing the patient.
Equipment
- Ordinary bed equipment,
- Extra sheet,
- Extra blanket,
- Soft pillow with rubber mackintosh cover,
- cradle if needed,
- Sand bags if needed,
- Emergency dressing trolley and tourniquets.
Procedure
- Prepare the foundation of the bed as usual.
- To make the lower half, use one sheet and blanket, for upper also, one top sheet and blanket.
- The two sections of the top linen should overlap each other at least 8 to 10 inches. So that it can be easily lifted to observe the stump.
- Elevate the stump over the soft pillow covered with mackintosh.
- Place sand bags on either side of the sumps to prevent it from jerking.
- Bed cradles are used to take up the weight of the bed linen.
- Cover the patient and make the unit tidy.
Striker Bed
It is a bed consisting of two frames one anterior and one posterior, which are attached to the main structure and may be turned through 180° thus allowing the patient to lie either prone or supine.
Purposes
- To immobilize following spinal injury.
- To maintain cervical traction.
- To allow change of position and to prevent bed sore in any patient with a spinal lesion.
Traction Bed Making
Making a comfortable bed when patient is in traction
Purposes
- To provide clean and comfortable bed to the patient.
- To maintain position of patient and traction
- To aid in immobilize the fracture part.
Cradle Bed Making
It is a bed with a cradle to carry the weight of the bed clothes.
Purposes
- To protect an affected part from the weight of the upper bedding.
- To protect the upper bedding from moist.
- To prevent infection to the burn area.
Procedure
- Make the foundation of the bed i.e. only bottom of bedding.
- Place a cradle in the position over the part of the portion the patient to be protected.
- Place the top sheet over the cradle and let it come over the chest of the patient.ilqa
- Place a blanket up well about the patient's shoulders. Tuck it in smoothly at foot and make corners under the mattress. Make sure that the patient is adequately warm.
- Replace the pillow.
- Leave the patient in comfort.
Different Positions and Their Uses
Positioning is defined as planning the person in a proper body alignment for the purpose of preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative aspects of health or placing the patient in good body alignment as needed therapeutically. It is one of the basic procedures that nursing personnel perform most frequently.
Purposes
- To promote comfort and relaxation to the patient.
- To relieve pressure on various parts.
- To stimulate circulation.
- To improves gastrointestinal function.
- To allows for greater lung expansion and improves respiratory function.
- To provide proper body alignment.
- To carryout nursing interventions.
- To perform surgical & medical investigations.
- To prevent complications caused by immobility.
- To promote normal physiological functions.
Principles
- Maintain good body mechanics.
- Wash hands before & after the procedure.
- Ensure the patient's comfort and safety.
- Follow the systematic and orderly way of doing.
- Use right technique at right time.
- Properly handle the patient's body to prevent pain or injury.
- Obtain assistance, if needed, to move heavy or helpless patients.
- Ensure that sheets are clean and dry.
- Avoid placing a body part directly over another to prevent pressure.
- Plan a regular position change schedule for the patient for 24 hours.
- Follow specific physician's orders.
Types of Positions Used
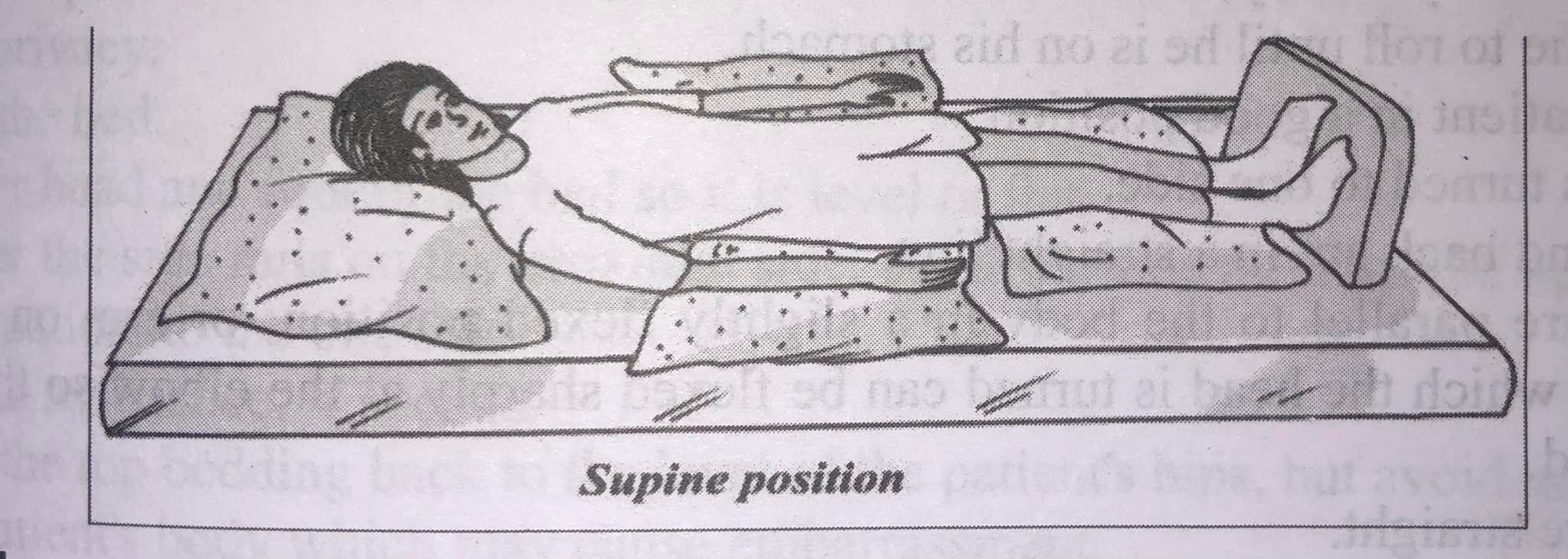
Supine/Dorsal/Back Laying
The patient lies on his back with his head and shoulders are slightly elevated. Pillows may be used under the head, knees for comfort. A foot support is used to prevent foot drop and maintain proper alignment. The risk of aspiration is greater with this position thus the supine position should be avoided when the client is confused, agitated, experiencing a decreased level of consciousness or at risk for aspiration.
Indications
- The usual position used by the patient.
- Used for examination of the chest and abdomen.
Procedure
- Explain the procedure.
- Collect equipment such as pillows, positioning aids as indicated.
- Wash hands.
- Provide privacy throughout the procedure.
- Position the bed.
- Place the bed in a flat or level position at working height, unless contraindicated.
- Lower the side rails on the proximal side (as necessary).
- Move the patient from a lateral (side) position to a supine position.
- For the patient on his side, remove supportive pillows.
- Fold top bedding back to the hips, being careful to avoid any undue exposure of the patient's body.
- With one hand on the patient's shoulder and one on the hip, roll his body in one piece (like a log) over onto his back.
- Align the patient's body in good position.
- Head, neck, and spine are in a straight line.
- Arms are at the patient's sides (parallel to the body) with hands prone.
- Legs are parallel to his body.
- Hips, knees, and feet should be in good alignment.
- Support the body parts in good alignment for comfort.
- Place a pillow under the head and shoulders to prevent strain on neck muscles and hyperextension and flexion of the neck.
- Put a footboard at the foot of the bed and place the feet flat against it (at right angles to the legs) to prevent plantar flexion ("foot drop").
- Place a pillow under each forearm so the arm is at least six inches from the body and reduce internal rotation of shoulder and extension of elbows.
- Place the air ring under the hips and cotton or foam pads under the heels to reduce the pressure. visise bas holm and it stand
- Place trochanter rolls/sand bags parallel to lateral surface of external rotation of hip.) the thighs. (reduces 38 supin
- Place small pillow under thighs it prevents hyper extension of knees
- If the patient is a paralyzed, place hand role in hand.
- Provide for the patient's comfort and safety.
- Replace the bedding neatly and raise the side rails, if used.
- Place the call light within reach.
- Position the bedside stand or bedside table so that the patient will be within easy reach of drinking water and personal items.
Problems to be Prevented
- Hyperextension of neck
- Posterior flexion of lumber curvature
- External rotation of legs bac
- Hyper extension of knees
- Planter flexion
- Pressure on heels
Prone Position
The prone position is a position in which the patient lies on the abdomen with the head turned to one side with one small pillow under the ankle. One soft pillow is given under the head.
Indications
- It can be used post operatively to prevent aspiration of saliva and mucous.
- Used in post-operative cases tonsils, vasico vaginal fistula and spinal cases.
- For patient with pressure sores, burns, injuries and operations on the back.
- For patients after 24 hours of amputation of lower limbs.
- To relieve abdomen distention.
- Position for renal biopsy.
- To examine the back.
Procedure
- Explain the procedure.
- Provide privacy.
- Wash your hands
- Collect the equipment:
- Pillows.
- Positioning aids as indicated.
- Adjust the bed.
- Lower the headrest and knee rest so that the bed is in a flat position.
- Raise the bed to working height.
- Lower the side rails on the side where you are working.
- Fold the top bedding down to the level of the patient's hips, but avoid undue exposure of the patient's body, which may cause embarrassment.
- Position the patient in bed.
- If there is room between the end of the mattress and the foot of the bed, the patient should be moved down in the bed so that his feet extend over the edge of the mattress.
- Remove the footboard if one is present.
- Turn the patient onto his side and then onto his stomach.
- Roll toward you so you can observe him closely.
- Continue to roll until he is on his stomach.
- Align the patient in a good position.
- Head is turned to one side.
- Neck and back are in a straight line.
- Arms are parallel to the body in a slightly flexed position; or arm on the same side toward which the head is turned can be flexed sharply at the elbow so the hand is near the head.
- Legs are straight.
- Feet are extended over the edge of the mattress or a pillow is placed under both ankles to prevent plantar flexion (foot drop) as a result of prolonged hyperextension.
- Support the patient's body and keep it in good alignment.
- A small pillow or folded towel under the head may be used to prevent hyperextension and flexion of the neck.
- A pillow under the abdomen provides comfort and prevents hyperextension of the lower spine.
- Provide comfort and safety to the patient.
- Replace bedding neatly.
- Raise and secure the side rails.
- Place the call light within reach.
_1671856540.jpg)
Problems to be Prevented
- Flexion/hyperextension of neck.
- Hyperextension of lumber curvature.
- Pressure on breasts, heels and genitals.
- Foot drop.
Things to remember
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google