Breeding
Subject: Science

Overview
Selective breeding has been the process of selecting and breeding plants and animals with desirable traits for agricultural goods since prehistoric times. This method introduces desirable traits into an organism and establishes those traits in subsequent offspring. However, it can lead to the genetic transmission of infectious diseases, congenital genetic abnormalities, and reduced biodiversity. Techniques for selective breeding include inbreeding, line breeding, self-pollination, and cross breeding. Cross-breeding involves mating two unrelated individuals to produce offspring with desired traits. Hybrids, such as lions, tigers, beefalos, zebroids, mules, and tomatoes, can be produced by crossing two distinct species within the same genus. Advantages of cross-breeding include blending advantageous traits from different species, using a variety of genetic material, generating higher-quality animals, and increasing crop yield. However, disadvantages include potential future issues with breeding policy, lower prices, export market restrictions, and an increased risk of purebred species extinction.
Selective Breeding
People have been choosing and breeding plants and animals with desirable traits for desired agricultural goods since prehistoric times. To put it another way, selective breeding is the process of choosing the finest plants and animals and then interbreeding them to produce children with the desired traits. Selective breeding is mostly used to introduce desirable features into an organism and establish those traits in subsequent offspring. In order to generate desirable plants and animals, this process entails selecting and breeding the mother and father, or both.By using the DNA variety that naturally exists in organisms, selective breeding promotes natural reproduction. On the other hand, some individuals object to it because they believe that some natural traits may be lost or mutated, leading to the appearance of undesirable traits in animals. For instance, if we only breed tall animals and exclude dwarf creatures, the progeny will have the tall gene. The characteristic of being tall will persist in subsequent generations, whereas the feature of being dwarf or short will vanish if this procedure is done many times.
Disadvantages of Selective Breeding
- Selective breeding typically results in an increase in the number of plants and animals with genetically similar features.
- The genetic transmission of infectious illnesses is a possibility.
- Because this procedure involves mating very closely related animals, there is a higher chance of congenital genetic abnormalities in the progeny.
- Because selective breeding includes human intervention, it is often referred to as artificial selection.
- Selective breeding can reduce biodiversity and block some naturally occurring genetic features, which increases the likelihood that some undesirable qualities will eventually drive a species to extinction.
Methods of Selective Breeding
Various techniques can be adopted in selective breeding. Some techniques are mentioned below:
Inbreeding
To create a population of organisms with dependable features, inbreeding is used. This approach permits interbreeding between animals that are closely related. Continuous inbreeding will result in genetically similar children. Inbred or purebred organisms are those created in this manner. Labrador Retriever dogs and Siamese cats are two examples of purebred animals.
Line Breeding
It's a form of inbreeding as well. By mating more distant cousins, this method produces animals with desirable traits. As a result, the rate of purebreeding declines. It also lessens the possibility of health problems that occasionally affect animals of purebred origin.
Self-pollination
The reproductive organs of most plants are located in the same body. They have the capacity to self-pollinate. Plants cultivated from self-pollinated seeds bear some, but not all, of their mother plant's characteristics. This results from the reordering of genes during sexual reproduction. Plants that are genetically similar can be produced using this procedure.
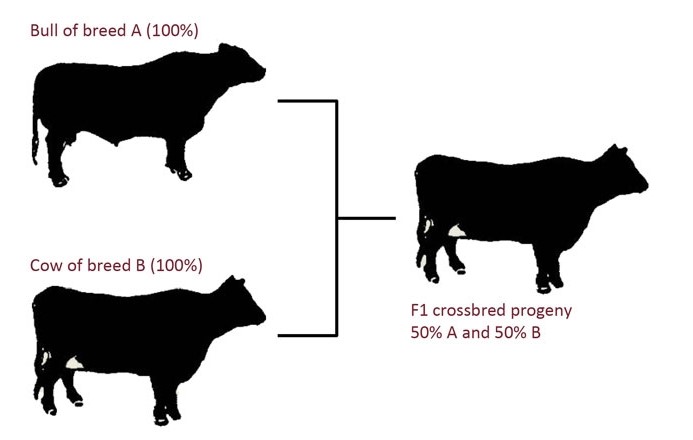
Cross Breeding
Breeding two unrelated individuals is the strategy used in this case. This kind of mating typically occurs between two distinct species within the same genus. This is frequently employed to create offspring from two distinct people that have the desired features. By mating two purebred creatures, this approach works well for producing offspring that exhibit the desired traits. Hybrids are progeny created via cross-breeding. The primary goal of cross-breeding is to improve the hybrid's quality. Not every subsequent generation inherits the hybrid's traits.
Some Organisms Produced from Cross Breeding
- Liger
The term "liger" refers to the hybrid animal created when a male lion and a female tiger are crossed. It is the most well-known animal hybrid. It surpasses parents in size. It acts like a lion most of the time.
- Tigon
Tigon is the name given to the hybrid animal created when a female lion and a male tiger are crossed. In comparison to the liger, Tigon is smaller than both of its parents together. Although it looks like a tiger, most of its traits—including roaring and socializing—come from lions.

- Beefalo
A bull and a buffalo (American bison) cross produces a hybrid known as a beefalo. Because they are able to procreate, they differ from other hybrids.

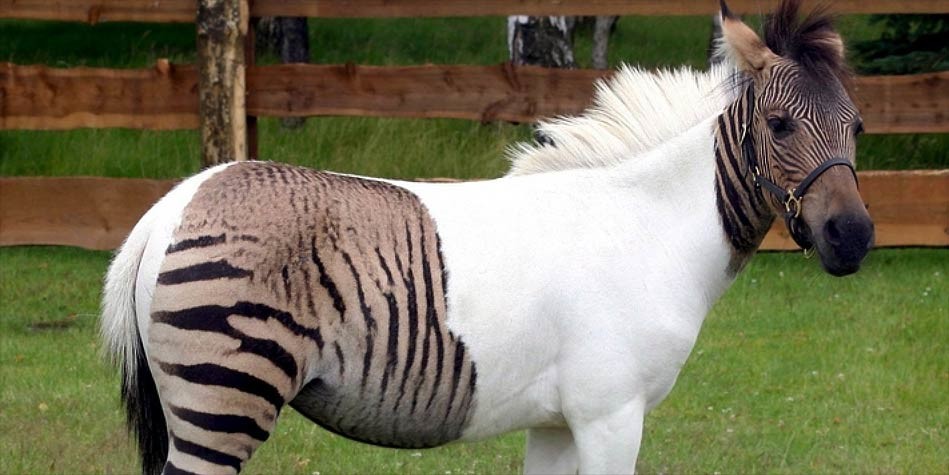
- Zebroid
Zebroids are the hybrid animals created when zebras and horses are crossed. They are unable to procreate.

- Mule
Mules are the hybrid animals created when a donkey and a horse are crossed. It can sprint like a horse and carry loads like a donkey. Moreover, it is sterile.

- Pomato
The plant created by crossing a tomato with a potato is called a tomato. Potatoes are grown underground in this plant, whereas tomatoes are produced on stems above the earth.
Advantages of Cross Breeding
It is possible to crossbreed both animals and plants. This technique can be used to create new species of organisms. Farmers gain by using this method. Below are a few benefits of cross-breeding:
- This technique blends the advantageous traits of two creatures from various species, breeds, or variations.
- It is possible for humans to create creatures with chosen traits.
- Cross-breeding can help with using a variety of genetic material.
- It is possible to generate animals that are of higher quality than their parents.
- This technique can enhance an organism's vigor, age, strength, immunity, etc.
- Plants grown using this strategy have the potential to boost crop yield.
Disadvantages of Cross Breeding
- Future issues with breeding policy may occur if cross-breeding procedures are not well understood and managed.
- Products derived from cross-breeding are less expensive than those derived from pure breeding. So, farmers' incomes fall short of their expectations.
- The export market restricts the selling of animals resulting from cross-breeding.
- The likelihood of purebreds going extinct rises as the hybrid's genetic and outward traits continue to change.
- Because the natural qualities of parents are not entirely passed down to their offspring in this breeding process, these traits may eventually disappear.
Things to remember
- Selective breeding has been a process of selecting and breeding plants and animals with desirable traits for agricultural goods since prehistoric times.
- Techniques used in selective breeding include inbreeding, line breeding, self-pollination, and cross breeding. Inbreeding allows for interbreeding between closely related animals, while line breeding produces offspring with desirable traits by mating distant cousins.
- Some well-known hybrid animals produced from cross-breeding include lions, tigers, beefalos, zebroids, mules, and tomatoes.
- Cross-breeding can enhance an organism's quality, increase crop yield, and provide a variety of genetic material.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.





 Login with google
Login with google