Blood Circulation in Human Body
Subject: Science

Overview
The human body has various organ systems, each with specific functions. The circulatory system, one of the nine systems, is responsible for facilitating the movement of chemicals throughout the body. Due to the pressure that the heart generates, blood—which consists of plasma and blood corpuscles—travels in a single direction. High blood pressure and cholesterol buildup can cause cardiac issues. The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, capillaries, veins, and arteries. Each system plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen, nutrients, waste materials, and carbon dioxide to the body's tissues and cells.
The human body has several organ systems. Every system carries out a certain function. Food gets broken down and transformed into more easily absorbed forms in the digestive tract. The body uses the circulatory system to carry these most basic forms, like glucose, to every cell. Hormones, oxygen, and medications are all moved throughout the body in a similar manner. Blood circulation is primarily responsible for facilitating the movement of chemicals throughout the human body. Blood is made up of plasma and blood corpuscles, and because of the pressure the heart creates as it pumps, blood only travels in one direction in our bodies. Blood pressure, which is felt in the arteries, is one type of pressure that the heart creates. Blood pressure might occasionally be higher than usual for a variety of reasons. High blood pressure and cholesterol buildup on the heart's wall and in the arteries are the causes of several cardiac issues. Heart issues can be treated using a variety of current technologies. For instance, open heart bypass surgery, angioplasty, etc. The human body is composed of four blood groups: A, B, AB, and O. Each blood group has the potential to be either Rh positive or Rh negative, so there are a total of eight blood groups, including Rh positive and Rh negative.
Human Blood Circulatory System
One of the nine systems in the human body is the circulatory system. Other systems are connected to this system as well. The heart, which pumps blood drawn from different regions of the body, is the main organ of the blood circulation system. All of our body's cells get the blood that the heart pumps through blood vessels. It carries oxygen from the air and nutrients to every cell in the human body. Similar to this, blood transports waste materials to excretory organs and carbon dioxide generated in cells to the lungs. The circulatory system's primary components are the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Blood Vessel
The musculoskeletal, flexible tubes called blood vessels carry blood to the body's many tissues and cells. The three different types of blood vessels are capillaries, veins, and arteries.
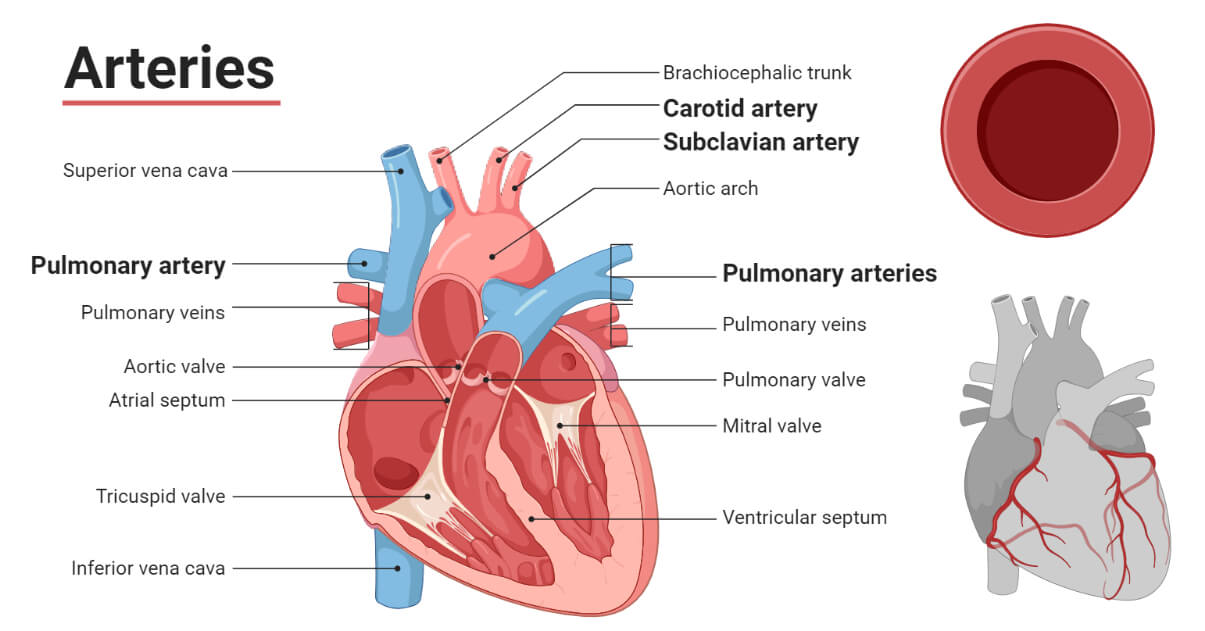
Artery
An artery is a blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to other regions of the body. Blood vessels with a lot of muscle make up arteries. Such a strong wall of muscle aids in blood pressure resistance. Arteries lack any kind of valve. The main artery in the human body, the aorta, separates into several smaller arteries. Arterioles are produced when the arteries split. Once more, each arteriole splits to create a little blood capillary network.
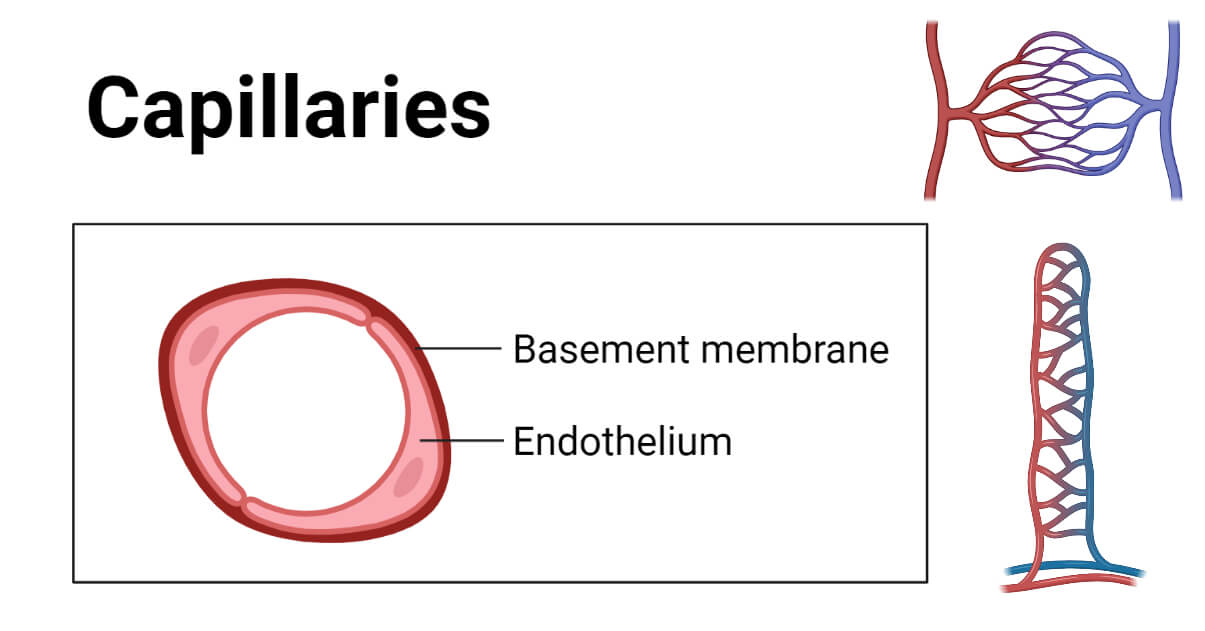
Capillaries
Capillaries are a network of tiny blood vessels that resemble hair or threads that are formed when arterioles split. Blood capillaries convey waste products like carbon dioxide, urea, and other needless compounds made in the cells to the excretory organs while also supplying the cells with nutrition, oxygen, hormones, enzymes, and other substances dissolved in blood. Venules and veins are formed when capillaries combine after absorbing waste products from the cell.
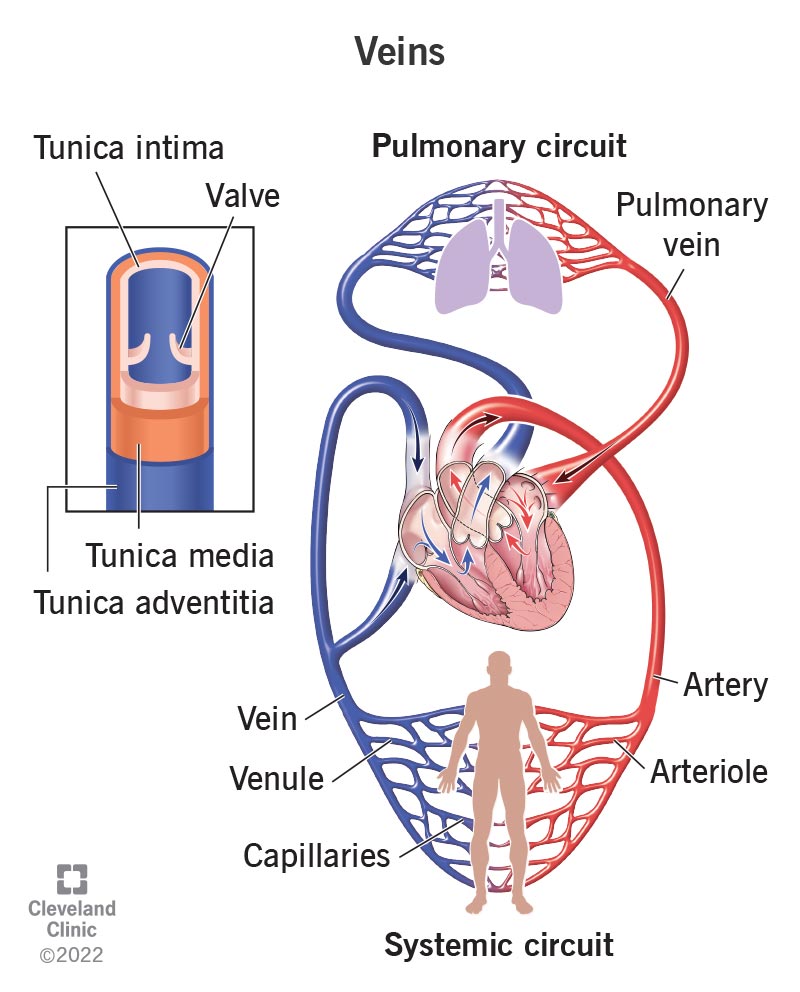
Vein
Veins are the blood vessels that carry blood from the body's organs to the heart. They feature a smaller layer of smooth muscles than arteries, but their wall is still made up of three layers.Thus, veins are blood tubes with thin walls. Because veins carry carbon dioxide and waste-rich blood gathered by venules to the heart, there is less blood in veins in terms of velocity and pressure as well as a decreased likelihood of blood flowing in the opposite direction. Veins have valves at regular intervals to stop blood flow in the opposite direction. Although they vary in size and quantity, the venacava, veins, and venules all serve a similar purpose.
Things to remember
- The circulatory system is one of the nine systems primarily responsible for the movement of chemicals throughout the body.
- Blood circulation, made up of plasma and blood corpuscles, is responsible for facilitating the movement of chemicals.
- Blood vessels, including capillaries, veins, and arteries, carry blood to tissues and cells.
- Arteries are blood vessels with a strong wall of muscle, aiding in blood pressure resistance.
- Capillaries are networks of tiny blood vessels that resemble hair or threads, transporting waste products to excretory organs and providing nutrients to cells.
- Veins, on the other hand, are blood vessels with thin walls and valves to prevent blood flow in the opposite direction.
- High blood pressure and cholesterol buildup on the heart's wall and arteries can cause cardiac issues.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.


 Login with google
Login with google