Study of the Universe
Subject: Science

Overview
Universe science focuses on understanding the past, present, and future of the universe, with astronomy being a subfield. The Big Bang Theory suggests that the universe was created through an enormous atomic explosion, causing galaxies to travel quickly and far apart. Astronomer Edwin Hubble's study in 1929 showed that galaxies are drifting apart, indicating that the universe is expanding. Hubble's law, which states that galaxies separate more quickly as they are farther apart, suggests that the constellations of the universe were once close to one another.
Have you ever wondered how the cosmos came to be? What kind of shape does the universe take?
Scientists have conducted several studies on it at various times concerning comparable questions. The field of study known as "universe science" focuses on learning more about the past, present, and future of the universe. Astrophysics, one of its subfields, investigates the beginning, nature, and future of the cosmos.
Big Bang Theory
Our solar system is located around 30,000 light years away from the Milky Way galaxy, a spiral galaxy with a diameter of 100,000 light years. According to mathematical calculations, this galaxy alone has 1.5 billion stars. The Big Bang idea is seen to be the most trustworthy of the many origins of the universe hypotheses that have been put forth. 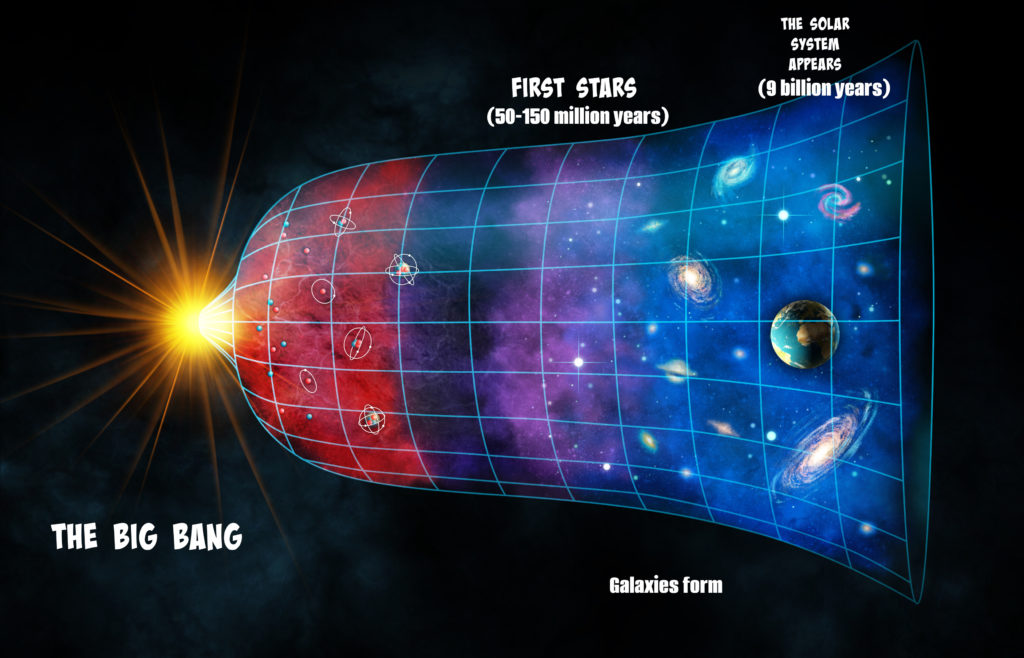 However, this hypothesis is said to have originated from the fact that all galaxies, including the Milky Way, are traveling very quickly and far apart from one another. Following this hypothesis, the enormous atomic explosion that gave rise to the cosmos is said to have occurred. Before the explosion, it was thought that the four fundamental forces of the universe—gravitation, electromagnetism, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force—had coalesced into one single force. The cosmos is therefore thought to have been very compressed at the earliest stage of existence. The cosmos was thought to have been the size of a minuscule single atom and incredibly active at that time. According to the Big Bang hypothesis, the universe was created when an enormous burst of atoms occurred as a result of excessive force and pressure. The genesis of every celestial body in the cosmos is said to have come from this explosion.
However, this hypothesis is said to have originated from the fact that all galaxies, including the Milky Way, are traveling very quickly and far apart from one another. Following this hypothesis, the enormous atomic explosion that gave rise to the cosmos is said to have occurred. Before the explosion, it was thought that the four fundamental forces of the universe—gravitation, electromagnetism, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force—had coalesced into one single force. The cosmos is therefore thought to have been very compressed at the earliest stage of existence. The cosmos was thought to have been the size of a minuscule single atom and incredibly active at that time. According to the Big Bang hypothesis, the universe was created when an enormous burst of atoms occurred as a result of excessive force and pressure. The genesis of every celestial body in the cosmos is said to have come from this explosion.
All of the heavenly bodies are traveling far apart from one another following the massive explosion of that dense atom, just as particles disperse and move away from one another after an explosive explosion. Therefore, the universe is getting bigger by the day. It continues to grow slowly but steadily. But because of gravity, these bodies' pace is slowing down.
Hubble's Study
 It has been found that the galaxies in outer space are drifting apart. Using the Mount Wilson 100-inch Hooker telescope, American astronomer Edwin Hubble attempted to determine the velocities of several galaxies in 1929 BC. He found out throughout his investigation that every galaxy in Hubble's connection between galaxies is advancing away from other galaxies of similar velocity and distance. According to his calculation, heavenly bodies look smaller the further they are from the earth. Additionally, they move at a higher velocity.
It has been found that the galaxies in outer space are drifting apart. Using the Mount Wilson 100-inch Hooker telescope, American astronomer Edwin Hubble attempted to determine the velocities of several galaxies in 1929 BC. He found out throughout his investigation that every galaxy in Hubble's connection between galaxies is advancing away from other galaxies of similar velocity and distance. According to his calculation, heavenly bodies look smaller the further they are from the earth. Additionally, they move at a higher velocity.
Then he illustrated the link between the velocities of the constellations and their distances by plotting their velocities against their distances on a graph. The equation 'v = Hd' serves as a representation of Hubble's law. Here, 'v' denotes the speed at which galaxies are separating from one another; d denotes their separation; and H denotes Hubble's constant. 73 km/s/Mpc [kilometer per second per mega parsec] is the value for this constant. This indicates that any two galaxies at a distance of one megaparsec are moving apart from one another at a speed of 73 km/s.
The velocity at which any two galaxies are moving apart may be calculated by taking the distance between them in milliseconds and multiplying it by Hubble's constant. We learned that the galaxies are traveling extremely far away, very fast, as a result of our computation. 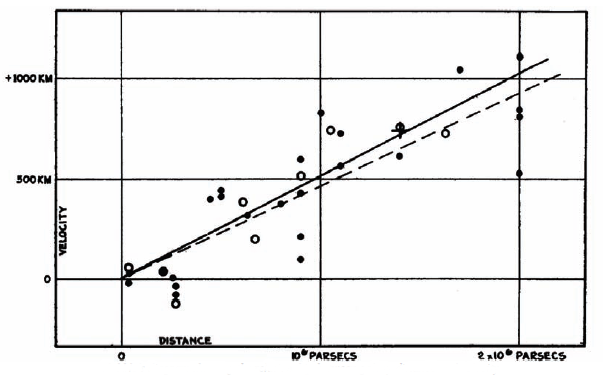 The Hubble equation also reveals that galaxies separate more quickly the further apart they are.
The Hubble equation also reveals that galaxies separate more quickly the further apart they are.
This suggests that the cosmos is expanding, just as every dot separates as the size of the air-filled balloon increases. The universe's constellations are drifting apart from one another. Consequently, it is reasonable to believe that they were once near one another, which implies that they were all at the same location a very long time ago. As a result, Hubble's research supports the Big Bang idea.
Things to remember
- Mathematical studies indicate that there are 1.5 billion stars in our galaxy alone.
- The Big Bang theory states that a massive explosion of atoms brought on by extreme pressure and force created the universe.
- It has been discovered that galaxies in space are separating from one another.
- The cosmos is expanding every day. It keeps expanding gradually yet steadily. But the speed of these bodies is decreasing due to gravity.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google